
Sure! Here’s a bilingual explanation (Hindi + English) of each concept related to Structures from your image — with examples where needed:
📘 Structures in C (स्ट्रक्चर इन C)
A structure is a user-defined data type used to group related data types together.
Structure एक ऐसा डेटा टाइप है जिसमें आप कई अलग-अलग प्रकार के डेटा को एक साथ रख सकते हैं।
✅ 1. Defining a Structure
English: Create a blueprint using struct.
Hindi: struct की मदद से एक structure टाइप बनाते हैं।
struct Student {
int roll;
char name[20];
float marks;
};
✅ 2. Declaring Structure Variables
English: After defining, create variables of the structure.
Hindi: Structure define करने के बाद, उसके टाइप के variables बनाते हैं।
struct Student s1, s2;
✅ 3. Accessing Structure Elements
English: Use the dot . operator.
Hindi: Dot (.) ऑपरेटर से structure के members को access करते हैं।
s1.roll = 101;
strcpy(s1.name, "Rahul");
s1.marks = 89.5;
✅ 4. Passing Structure to Functions (By Value & Reference)
🔹 By Value (कॉपी भेजना):
void display(struct Student s) {
printf("%d", s.roll);
}
🔹 By Reference (पता भेजना):
void display(struct Student *s) {
printf("%d", s->roll);
}
Hindi: Value से भेजने पर structure की कॉपी जाती है।
Reference से भेजने पर address भेजते हैं जिससे असली डेटा बदल सकता है।
✅ 5. Function Returning Structure
English: A function can return a structure.
Hindi: कोई function structure को return कर सकता है।
struct Student getStudent() {
struct Student s = {101, "Amit", 92.0};
return s;
}
✅ 6. Array of Structures
English: Store multiple structure variables.
Hindi: Structure के कई objects को array में स्टोर कर सकते हैं।
struct Student class[50];
✅ 7. Passing Array of Structures to Function
English: Send whole array as argument.
Hindi: Structure का पूरा array function को भेज सकते हैं।
void displayAll(struct Student s[], int n);
Would you like this in PDF/notes format for revision or practice questions too?
Computer lab:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// Declare a structure named "car"
struct car {
string brand;
string model;
int year;
};
int main() {
car myCar1, myCar2;
// Input for first car
cout << "Enter details for Car 1:\n";
cout << "Brand: ";
getline(cin, myCar1.brand);
cout << "Model: ";
getline(cin, myCar1.model);
cout << "Year: ";
cin >> myCar1.year;
cin.ignore(); // To clear the newline character from input buffer
// Input for second car
cout << "\nEnter details for Car 2:\n";
cout << "Brand: ";
getline(cin, myCar2.brand);
cout << "Model: ";
getline(cin, myCar2.model);
cout << "Year: ";
cin >> myCar2.year;
// Output
cout << "\nCar 1: " << myCar1.brand << " " << myCar1.model << " " << myCar1.year << "\n";
cout << "Car 2: " << myCar2.brand << " " << myCar2.model << " " << myCar2.year << "\n";
return 0;
}Output:
Enter details for Car 1:
Brand: Toyota
Model: Corolla Altis
Year: 2015
Enter details for Car 2:
Brand: Honda
Model: Civic
Year: 2018
Car 1: Toyota Corolla Altis 2015
Car 2: Honda Civic 2018

Here are bilingual exam notes (English + Hindi) based on the Object Oriented Programming (OOP) topics from your image.
📘 Object Oriented Programming (OOP) – Exam Notes
ऑब्जेक्ट ओरिएंटेड प्रोग्रामिंग – परीक्षा नोट्स
🔹 1. Concept of Object Oriented Programming
English: OOP is a programming paradigm based on the concept of “objects”.
Hindi: OOP एक प्रोग्रामिंग तरीका है जो “objects” के कॉन्सेप्ट पर आधारित होता है।
🔹 2. Data Hiding
English: Restricting access to internal details of an object.
Hindi: किसी object के अंदर की जानकारी को छुपाना।
Example: Using
privatekeyword.
🔹 3. Data Encapsulation
English: Wrapping data and functions together into one unit (class).
Hindi: डेटा और functions को एक साथ एक यूनिट (class) में बाँधना।
Example: A class that contains both variables and methods.
🔹 4. Class and Object
Class
- English: A blueprint or template to create objects.
- Hindi: Objects बनाने के लिए एक खाका (template)।
Object
- English: An instance of a class.
- Hindi: Class का एक असली उदाहरण (object)।
class Car {
public:
string brand;
};
Car myCar; // object
🔹 5. Abstract Class and Concrete Class
Abstract Class
- English: A class with at least one pure virtual function.
- Hindi: जिसमें कम से कम एक pure virtual function हो।
Cannot be instantiated directly.
Concrete Class
- English: A class that can be instantiated and has complete definitions.
- Hindi: पूरी तरह से defined class जिसे object बनाया जा सकता है।
🔹 6. Polymorphism
English: Same function behaves differently in different situations.
Hindi: एक ही नाम का function अलग-अलग तरीकों से काम करता है।
➤ Function Overloading (C++ Example)
Multiple functions with same name but different parameters.
int add(int a, int b);
float add(float x, float y);
🔹 7. Inheritance
English: A class can inherit properties of another class.
Hindi: एक class दूसरी class की properties को प्राप्त कर सकती है।
class Animal {
public:
void speak();
};
class Dog : public Animal {};
🔹 8. Advantages of OOP over Earlier Programming
| Feature | OOP | Earlier (Procedural) |
|---|---|---|
| Reusability | ✅ | ❌ |
| Data Hiding | ✅ | ❌ |
| Scalability | ✅ | ❌ |
| Modularity | ✅ | ❌ |
Hindi Summary:
OOP में code reuse होता है, security मिलती है, और maintenance आसान होता है।

📘 Implementation of OOP Concepts in C++
C++ में ऑब्जेक्ट ओरिएंटेड प्रोग्रामिंग के कांसेप्ट का कार्यान्वयन
✅ 1. Definition of a Class (क्लास की परिभाषा)
English: A class is a blueprint that defines data members and member functions.
Hindi: क्लास एक ढाँचा (blueprint) है जिसमें डेटा और फंक्शन होते हैं।
class Student {
int roll; // data member
public:
void getData(); // member function
};
✅ 2. Members of a Class (क्लास के मेंबर्स)
- Data Members: Variables inside a class. (क्लास के अंदर के वेरिएबल्स)
- Member Functions: Functions defined inside a class. (क्लास के अंदर के फंक्शन)
✅ 3. Visibility Modes – Public & Private
English: Controls access to class members.
Hindi: क्लास मेंबर्स को कौन access कर सकता है, यह तय करता है।
private: accessible only inside the classpublic: accessible from outside the class
class A {
private:
int x;
public:
void setX(int val) { x = val; }
};
Note: By default, members in a class are private.
✅ 4. Member Function Definition
➤ Inside Class Definition
class A {
public:
void show() {
cout << "Hello";
}
};
➤ Outside Class Definition (Using Scope Resolution ::)
class A {
public:
void show();
};
void A::show() {
cout << "Hello";
}
✅ 5. Declaration of Objects (ऑब्जेक्ट बनाना)
English: Object is an instance of a class.
Hindi: Object, class का असली उपयोग (instance) होता है।
Student s1, s2;
✅ 6. Accessing Members from Objects (ऑब्जेक्ट से डेटा एक्सेस करना)
s1.setData(); // calling public member function
✅ 7. Array of Objects (ऑब्जेक्ट्स का ऐरे)
English: Store multiple objects using an array.
Hindi: कई objects को एक array में स्टोर किया जाता है।
Student arr[10];
✅ 8. Objects as Function Arguments (फंक्शन में ऑब्जेक्ट भेजना)
➤ Pass by Value (कॉपी भेजना):
void display(Student s);
➤ Pass by Reference (असली डेटा भेजना):
void display(Student &s);

It looks like you’ve shared an image with information on constructors and destructors. I’ll provide notes in both Hindi and English based on this. Here’s the summary:
Constructor and Destructor (in English):
Constructor:
- Special Characteristics: A constructor is a special member function that is automatically called when an object is created.
- Declaration and Definition: It is defined with the same name as the class and does not return any type.
class MyClass {
public:
int data;
// Default constructor
MyClass() {
data = 0;
}
// Parameterized constructor
MyClass(int value) {
data = value;
}
};
- Types:
- Default Constructor: A constructor that takes no parameters.
- Overloaded Constructors: Multiple constructors with different parameter lists.
- Copy Constructor: A constructor that creates a new object as a copy of an existing object.
- Constructor with Default Arguments: A constructor that uses default values for some parameters if no value is provided.
Lab
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
// Constructor of the class without
// any parameters
A() {
cout << "Constructor called" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
A obj1;
return 0;
} Destructor:
- Special Characteristics: A destructor is called when an object is destroyed.
- Declaration and Definition: It is defined with the same name as the class but with a tilde (~) prefix.
class MyClass {
public:
MyClass() {
data = new int; // Allocate memory
}
~MyClass() {
delete[] data; // Release the allocated memory
}
private:
int* data;
};
Inheritance (Extending Classes):
- Concept of inheritance allows a class to inherit attributes and methods from another class.
Constructor and Destructor (in Hindi):
Constructor (निर्माता):
- विशेष लक्षण: एक निर्माता एक विशेष सदस्य कार्य है जो स्वचालित रूप से तब बुलाया जाता है जब एक वस्तु बनाई जाती है।
- घोषणा और परिभाषा: इसे उस कक्षा (class) के समान नाम के साथ परिभाषित किया जाता है और यह कोई प्रकार (type) वापस नहीं करता।
- प्रकार:
- डिफ़ॉल्ट निर्माता (Default Constructor): एक निर्माता जो कोई पैरामीटर नहीं लेता।
- अधिभारित निर्माता (Overloaded Constructor): विभिन्न पैरामीटर सूची के साथ कई निर्माता।
- कॉपी निर्माता (Copy Constructor): एक निर्माता जो एक मौजूदा वस्तु की प्रति के रूप में एक नई वस्तु बनाता है।
- डिफ़ॉल्ट तर्क वाले निर्माता (Constructor with Default Arguments): एक निर्माता जो यदि कोई मान प्रदान नहीं किया जाता है तो कुछ पैरामीटर के लिए डिफ़ॉल्ट मान का उपयोग करता है।
Destructor (विनाशक):
- विशेष लक्षण: एक विनाशक तब बुलाया जाता है जब एक वस्तु नष्ट होती है।
- घोषणा और परिभाषा: इसे कक्षा के समान नाम के साथ परिभाषित किया जाता है लेकिन एक टिल्ड (~) प्रतीक के साथ।
Inheritance (विरासत / वर्गों का विस्तार):
- विरासत की अवधारणा यह अनुमति देती है कि एक कक्षा दूसरी कक्षा से गुण और विधियाँ (methods) प्राप्त करे।

Based on the image you shared, here’s the summary in both Hindi and English regarding inheritance and extending classes:
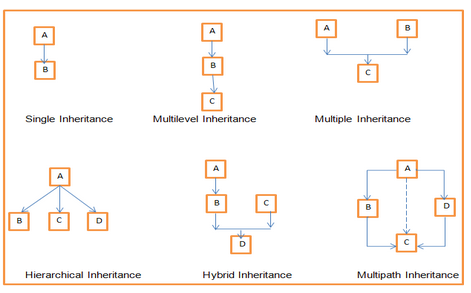
Inheritance (Extending Classes) – English:
Concept of Inheritance:
- Base Class: The class from which other classes inherit properties and methods.
- Derived Class: The class that inherits the properties and methods from the base class.
- Defining Derived Classes: A derived class is defined using the syntax that inherits from the base class.
Visibility Modes:
- Protected Visibility Mode: Members declared as protected can be accessed by the derived class, but not by outside code.
Types of Inheritance:
- Single-Level Inheritance: A class inherits directly from another class.
- Multilevel Inheritance: A class is derived from another derived class, forming a chain.
- Multiple Inheritance: A class inherits from multiple base classes.
Derived Class Types:
- Privately Derived: Members of the base class are inherited privately and are not accessible directly from outside.
- Publicly Derived: Members of the base class are inherited publicly, meaning they can be accessed by outside code.
- Protectedly Derived: Members of the base class are inherited with protected visibility.
Accessibility:
- The accessibility of base class members can vary depending on the derived class’s access level (private, public, or protected).
Inheritance (Extending Classes) – Hindi:
विरासत (Inheritance) का सिद्धांत:
- बेस कक्षा (Base Class): वह कक्षा जिससे अन्य कक्षाएँ गुण और विधियाँ (methods) विरासत में प्राप्त करती हैं।
- व्युत्पन्न कक्षा (Derived Class): वह कक्षा जो बेस कक्षा से गुण और विधियाँ प्राप्त करती है।
- व्युत्पन्न कक्षाएँ परिभाषित करना (Defining Derived Classes): एक व्युत्पन्न कक्षा को परिभाषित करते समय बेस कक्षा से विरासत प्राप्त की जाती है।
दृश्यता मोड (Visibility Modes):
- संरक्षित दृश्यता मोड (Protected Visibility Mode): संरक्षित रूप से घोषित किए गए सदस्य व्युत्पन्न कक्षा द्वारा एक्सेस किए जा सकते हैं, लेकिन बाहरी कोड से नहीं।
विरासत के प्रकार (Types of Inheritance):
- एकल-स्तरीय विरासत (Single-Level Inheritance): एक कक्षा दूसरी कक्षा से सीधे विरासत प्राप्त करती है।
- बहु-स्तरीय विरासत (Multilevel Inheritance): एक कक्षा दूसरी व्युत्पन्न कक्षा से विरासत प्राप्त करती है, जिससे एक श्रृंखला बनती है।
- बहुविकल्पी विरासत (Multiple Inheritance): एक कक्षा कई बेस कक्षाओं से विरासत प्राप्त करती है।
व्युत्पन्न कक्षाओं के प्रकार (Derived Class Types):
- निजी रूप से व्युत्पन्न (Privately Derived): बेस कक्षा के सदस्य निजी रूप से विरासत में प्राप्त होते हैं और बाहरी से सीधे पहुँच योग्य नहीं होते।
- सार्वजनिक रूप से व्युत्पन्न (Publicly Derived): बेस कक्षा के सदस्य सार्वजनिक रूप से विरासत में प्राप्त होते हैं और बाहरी कोड से एक्सेस किए जा सकते हैं।
- संरक्षित रूप से व्युत्पन्न (Protectedly Derived): बेस कक्षा के सदस्य संरक्षित दृश्यता के साथ विरासत में प्राप्त होते हैं।
सदस्यों की पहुँच (Accessibility):
- बेस कक्षा के सदस्यों की पहुँच व्युत्पन्न कक्षा के एक्सेस स्तर (निजी, सार्वजनिक, या संरक्षित) पर निर्भर करती है।
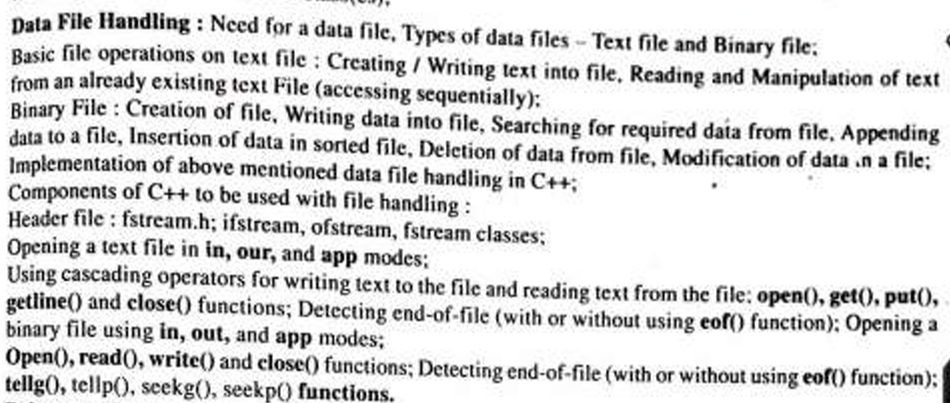
Here’s a summary of the content regarding Data File Handling in both English and Hindi:
Data File Handling – English:
Need for a Data File:
- Data files are needed to store data for later use, enabling easy access and manipulation.
Types of Data Files:
- Text File: Stores data in a human-readable format. Operations include reading, writing, and manipulating text.
- Binary File: Stores data in binary format, which is not human-readable but more efficient in terms of storage and speed.
Basic File Operations:
- Text File: Creating/writing text into a file, reading and manipulating text (accessing sequentially).
- Binary File: Creation of the file, writing data into it, searching for required data, appending data, and deletion or modification of data.
Components of C++ to Handle Files:
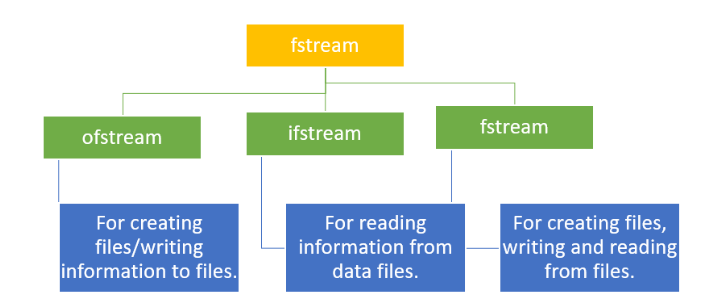
- Header File:
fstream.h,ifstream,ofstream,fstreamclasses.
File Handling Functions:
- Opening Files: Use modes like
in,out, andappto open text or binary files. - File Operations:
open(),get(),put(),getline(), andclose()functions are used for reading and writing text files. Theeof()function detects the end of the file. - Binary File Operations: Using modes like
in,out, andappfor binary files. Functions likeOpen(),read(),write(),close(),tellg(),tellp(),seekg(), andseekp()are used for binary file operations.
Data File Handling – Hindi:
डेटा फ़ाइल की आवश्यकता (Need for a Data File):
- डेटा फ़ाइलों की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि डेटा को बाद में उपयोग के लिए संग्रहीत किया जा सके, जिससे उसे आसानी से एक्सेस और संसाधित किया जा सके।
डेटा फ़ाइलों के प्रकार (Types of Data Files):
- टेक्स्ट फ़ाइल (Text File): यह डेटा को मानव-पठनीय रूप में संग्रहीत करती है। इसमें लेखन, पढ़ाई और डेटा का हेरफेर शामिल है।
- बाइनरी फ़ाइल (Binary File): यह डेटा को बाइनरी रूप में संग्रहीत करती है, जो मानव-पठनीय नहीं होता, लेकिन संग्रहण और गति के मामले में अधिक कुशल होता है।
बेसिक फ़ाइल ऑपरेशंस (Basic File Operations):
- टेक्स्ट फ़ाइल: फ़ाइल में लेखन, पढ़ाई और डेटा का हेरफेर (क्रम से एक्सेस करना)।
- बाइनरी फ़ाइल: फ़ाइल का निर्माण, उसमें डेटा लिखना, आवश्यक डेटा की खोज करना, डेटा जोड़ना, और डेटा को हटाना या संशोधित करना।
C++ में फ़ाइल हैंडलिंग के लिए घटक (Components of C++ to Handle Files):
- हेडर फ़ाइल (Header File):
fstream.h,ifstream,ofstream,fstreamकक्षाएँ।
फ़ाइल हैंडलिंग फ़ंक्शन (File Handling Functions):
- फ़ाइल खोलना (Opening Files):
in,out, औरappमोड का उपयोग करके टेक्स्ट या बाइनरी फ़ाइलों को खोला जाता है। - फ़ाइल ऑपरेशंस (File Operations): टेक्स्ट फ़ाइलों के लिए
open(),get(),put(),getline(), औरclose()फ़ंक्शन का उपयोग किया जाता है।eof()फ़ंक्शन का उपयोग फ़ाइल के अंत का पता लगाने के लिए किया जाता है। - बाइनरी फ़ाइल ऑपरेशंस (Binary File Operations): बाइनरी फ़ाइलों के लिए
in,out, औरappमोड का उपयोग किया जाता है।Open(),read(),write(),close(),tellg(),tellp(),seekg(), औरseekp()जैसी फ़ंक्शन का उपयोग बाइनरी फ़ाइल ऑपरेशंस के लिए किया जाता है।

Here is a summary of the content related to Pointers based on the image you provided, in both English and Hindi:
Pointers – English:
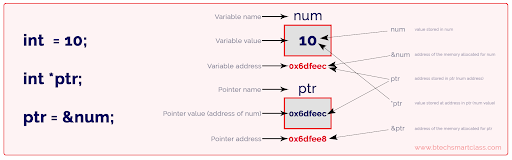
Declaration and Initialization of Pointers:
- Pointers are variables that store memory addresses of other variables.
- A pointer is declared with an asterisk (*) symbol before the variable name.
Dynamic Memory Allocation/Deallocation Operations:
- new: Used to allocate dynamic memory at runtime.
- delete: Used to deallocate or free memory allocated using
new.
Pointers and Arrays:
- Array of Pointers: An array where each element is a pointer.
- Pointer to an Array: A pointer that points to an array (1-dimensional array).
Function Returning a Pointer:
- A function can return a pointer, which can point to dynamically allocated memory or data.
Reference Variables and Use of Aliases:
- A reference variable is another name for an existing variable, providing an alias for it.
- Used in scenarios where you want to refer to a variable by another name.
Function Call by Reference:
- Passing a function argument by reference allows the function to modify the original variable’s value.
Pointer to Structures:
- Dereference Operator: The asterisk (*) is used to dereference a pointer and access the value it points to.
- Arrow Operator (->): Used to access members of a structure through a pointer.
- Self-Referential Structures: A structure that contains a pointer to an instance of the same structure (commonly used for linked lists).
Pointers – Hindi:
पॉइंटर की घोषणा और प्रारंभिककरण (Declaration and Initialization of Pointers):
- पॉइंटर वे चर (variables) होते हैं जो अन्य चर के मेमोरी पते को संग्रहीत करते हैं।
- एक पॉइंटर को घोषित करते समय उसके नाम से पहले एक एस्टेरिस्क (*) चिह्न का उपयोग किया जाता है।
डायनेमिक मेमोरी आवंटन / अवनति संचालन (Dynamic Memory Allocation/Deallocation Operations):
- new: रनटाइम पर डायनेमिक मेमोरी आवंटित करने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।
- delete:
newके द्वारा आवंटित मेमोरी को अवनत (deallocate) करने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।
पॉइंटर और ऐरे (Pointers and Arrays):
- पॉइंटर का ऐरे (Array of Pointers): एक ऐरे जिसमें प्रत्येक तत्व एक पॉइंटर होता है।
- ऐरे को पॉइंटर (Pointer to an Array): एक पॉइंटर जो एक ऐरे (1-आयामी ऐरे) की ओर इशारा करता है।
फ़ंक्शन जो पॉइंटर लौटाता है (Function Returning a Pointer):
- एक फ़ंक्शन एक पॉइंटर लौटाता है, जो डायनेमिक रूप से आवंटित मेमोरी या डेटा को इंगीत कर सकता है।
रेफेरेंस वेरिएबल्स और उपनाम का उपयोग (Reference Variables and Use of Aliases):
- एक रेफेरेंस वेरिएबल किसी मौजूदा वेरिएबल का दूसरा नाम होता है, जिससे उसे एक और नाम से संदर्भित किया जा सकता है।
- इसका उपयोग तब किया जाता है जब आप किसी वेरिएबल को दूसरे नाम से संदर्भित करना चाहते हैं।
फ़ंक्शन कॉल द्वारा संदर्भ (Function Call by Reference):
- जब किसी फ़ंक्शन को संदर्भ द्वारा एक तर्क (argument) पास किया जाता है, तो फ़ंक्शन मूल वेरिएबल के मान को बदल सकता है।
संरचनाओं के लिए पॉइंटर (Pointer to Structures):
- डिरेफरेंस ऑपरेटर (Dereference Operator): एस्टेरिस्क (*) का उपयोग पॉइंटर को डिरेफरेंस करने और जिस मान की ओर वह इशारा कर रहा है, तक पहुंचने के लिए किया जाता है।
- एरो ऑपरेटर (Arrow Operator, ->): जब पॉइंटर के माध्यम से संरचना के सदस्य तक पहुँचने के लिए इसका उपयोग किया जाता है।
- स्वयं-संदर्भित संरचनाएँ (Self-Referential Structures): एक संरचना जिसमें उसी संरचना के एक उदाहरण का पॉइंटर होता है (आमतौर पर लिंक्ड लिस्ट के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है)।
Let me know if you need further clarifications or more information!
